Top 5 Business VoIP Integration Challenges & Solutions
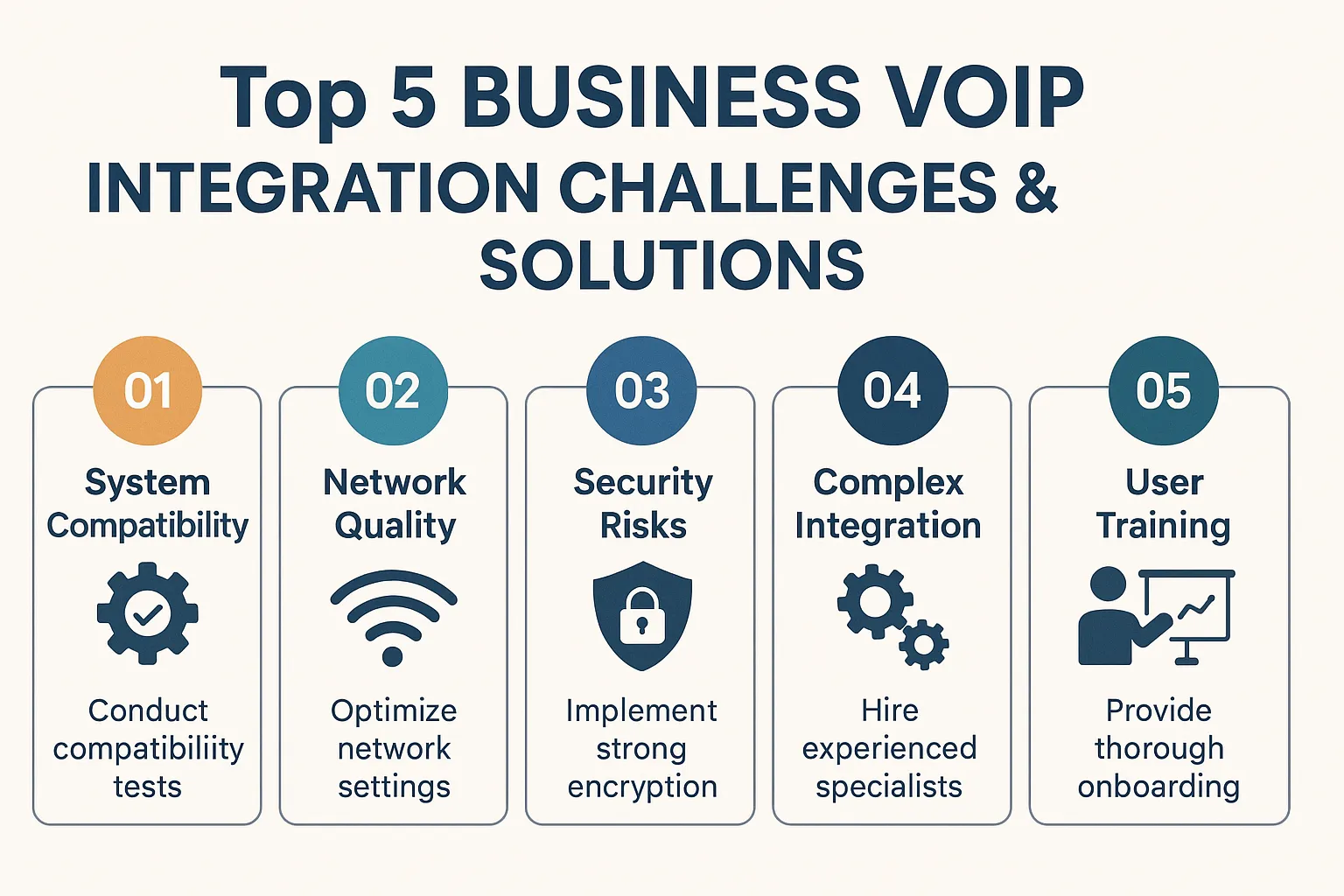
Switching to Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP) can transform how your business communicates, but the integration process often comes with hurdles. Many organizations struggle with technical compatibility, network requirements, and staff adaptation during the transition. Understanding these challenges before implementation helps you prepare effective solutions and ensures a smoother migration.
This guide explores the five most common VoIP integration obstacles businesses face and provides practical strategies to overcome them.
1. Legacy System Compatibility Issues
The Challenge
One of the biggest roadblocks during VoIP integration is connecting new phone systems with existing business infrastructure. Many companies rely on older Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software, or proprietary applications that weren’t designed to work with modern VoIP solutions. This incompatibility can disrupt workflows and limit the benefits of your new communication system.
Legacy hardware like analog phones, fax machines, and traditional Private Branch Exchange (PBX) systems often cannot interface directly with VoIP networks. When your old technology doesn’t communicate with new systems, you face data silos, lost productivity, and frustrated employees.
The Solution
Start by conducting a comprehensive audit of your current technology stack. Document every system, application, and hardware device that needs to connect with your new VoIP platform. This inventory helps you identify potential compatibility gaps early.
Choose a VoIP provider that offers robust Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and pre-built integrations with popular business software. Many modern VoIP solutions include native connections to platforms like Salesforce, Microsoft Teams, HubSpot, and Zendesk. These ready-made integrations eliminate much of the technical heavy lifting.
For legacy hardware, consider using Analog Telephone Adapters (ATAs) that bridge the gap between traditional analog devices and digital VoIP networks. These adapters allow you to keep functioning equipment while still moving to internet-based calling. Alternatively, develop a phased replacement strategy that gradually retires incompatible hardware as budget allows.
Working with experienced integration specialists or consultants can also accelerate the process. They bring expertise in connecting diverse systems and can often solve complex compatibility problems that internal teams struggle with.
2. Network Bandwidth and Quality of Service Concerns
The Challenge
VoIP systems depend entirely on your internet connection to function. Unlike traditional phone lines that operate independently, VoIP calls compete for bandwidth with all your other online activities including video conferences, file transfers, cloud applications, and web browsing. Insufficient bandwidth leads to poor call quality with symptoms like choppy audio, delays, dropped calls, and echo effects.
The problem intensifies during peak usage times when multiple employees make simultaneous calls or when large file transfers saturate your network. Poor Quality of Service (QoS) configurations can result in VoIP traffic getting deprioritized, making business communications unreliable precisely when you need them most.
The Solution
Begin by calculating your actual bandwidth requirements based on your business needs. A general rule suggests allocating approximately 100 kilobits per second (kbps) for each concurrent VoIP call, though this varies by codec. Add buffer capacity to account for growth and unexpected usage spikes.
Conduct network assessments using VoIP readiness tests available from many providers. These tools measure your current bandwidth, latency, jitter, and packet loss to determine if your network can handle VoIP traffic reliably. If testing reveals deficiencies, consider upgrading your internet service plan before implementing VoIP.
Implement Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your network routers and switches. QoS protocols prioritize VoIP packets over less time-sensitive data, ensuring voice traffic receives the bandwidth it needs even during network congestion. Configure your equipment to tag and prioritize Real-Time Protocol (RTP) traffic used by VoIP systems.
Consider establishing a dedicated internet connection exclusively for VoIP traffic if your business handles high call volumes. This separation guarantees that voice communications never suffer regardless of other network activities. While this increases costs, it provides maximum reliability for mission-critical business communications.
Network monitoring tools help you track performance continuously. Set up alerts for bandwidth utilization thresholds, packet loss, and latency spikes so you can address issues proactively before they impact call quality.
3. Security and Compliance Vulnerabilities
The Challenge
Moving communications to internet protocol networks exposes your business to new security risks. VoIP systems face threats including eavesdropping, toll fraud, denial of service attacks, call interception, and voice phishing (vishing). Hackers can exploit poorly secured VoIP networks to make unauthorized international calls, steal sensitive information shared during conversations, or disrupt business operations.
Regulatory compliance adds another layer of complexity. Industries like healthcare, finance, and legal services must meet strict data protection requirements such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR. VoIP implementations need proper encryption, access controls, and audit trails to satisfy these regulations. Failure to maintain compliance can result in severe penalties and reputational damage.
The Solution
Select a VoIP provider that prioritizes security with end-to-end encryption for all voice and video communications. Look for support of Transport Layer Security (TLS) for signaling and Secure Real-time Transport Protocol (SRTP) for media streams. These encryption standards protect your conversations from interception.
Implement strong authentication mechanisms including multi-factor authentication (MFA) for accessing VoIP administration panels and user accounts. Regularly update all passwords and enforce complexity requirements. Create role-based access controls that limit system permissions based on job functions.
Deploy Session Border Controllers (SBCs) at your network perimeter. These devices act as gatekeepers, filtering VoIP traffic and blocking malicious connection attempts. SBCs also hide your internal network topology from potential attackers and provide additional layers of defense.
Keep all VoIP software, firmware, and related systems current with security patches. Enable automatic updates where possible and establish regular maintenance schedules for manual updates. Vulnerabilities in outdated systems are common entry points for attackers.
For regulated industries, verify that your VoIP provider offers compliance-specific features such as call recording with retention policies, encrypted storage, and detailed audit logs. Obtain documentation of their security certifications and compliance attestations. Consider providers who undergo regular third-party security audits.
Educate employees about VoIP-specific threats like vishing attacks and social engineering attempts conducted through phone systems. Regular security awareness training reduces the risk of human error compromising your communications infrastructure.
4. Staff Training and Change Management Resistance
The Challenge
Even the most technically sound VoIP implementation can fail if employees don’t adopt it effectively. Many workers feel comfortable with familiar phone systems they’ve used for years and resist learning new interfaces and features. This resistance stems from fear of the unknown, concerns about productivity during the learning curve, and general change fatigue in organizations undergoing multiple technology transitions.
Without proper training, employees underutilize VoIP features like call routing, voicemail-to-email, video conferencing, and CRM integration. This underutilization means you don’t realize the return on investment from your new system. Frustrated users may also find workarounds that bypass the VoIP system entirely, creating communication silos and security gaps.
The Solution
Start change management efforts before the technical implementation begins. Communicate clearly about why the organization is moving to VoIP, emphasizing benefits that directly impact employees like remote work capabilities, easier call transfers, and unified communications. Address concerns openly and involve staff in planning decisions where appropriate.
Develop a comprehensive training program with multiple learning formats to accommodate different preferences. Include live instructor-led sessions for complex features, recorded video tutorials for self-paced learning, quick reference guides for desk-side assistance, and hands-on practice opportunities in a sandbox environment.
Identify and train power users or departmental champions before the full rollout. These early adopters can provide peer support, answer questions, and demonstrate effective use cases within their teams. Peer learning often resonates more than top-down training mandates.
Phase your implementation rather than switching everyone simultaneously. Start with a pilot group of tech-savvy employees who can provide feedback and help refine your training approach. Gradual rollouts allow your IT support team to manage issues without becoming overwhelmed.
Make ongoing support easily accessible through multiple channels including help desk tickets, chat support, FAQ documentation, and regular office hours where employees can ask questions. Celebrate early successes and share use cases that demonstrate the value of the new system.
Schedule refresher training sessions several weeks after initial implementation when users have encountered real-world scenarios and developed specific questions. This second wave of education addresses practical challenges that weren’t apparent during initial training.
5. Call Quality and Reliability Problems
The Challenge
Nothing frustrates customers and employees more than unreliable phone service. VoIP systems can experience various quality problems including one-way audio where only one person can hear, robotic or garbled voices, significant delays causing people to talk over each other, and complete call drops. These issues damage your professional image and can cost you business opportunities.
Reliability concerns also arise regarding power outages and internet disruptions. Traditional landlines continue functioning during power failures, but VoIP systems depend on electricity and internet connectivity. Businesses worried about maintaining communication during emergencies may hesitate to fully commit to VoIP solutions.
The Solution
Address network infrastructure issues that cause quality problems. Replace outdated routers and switches with equipment designed to handle VoIP traffic. Use wired Ethernet connections instead of wireless networks for desk phones whenever possible, as WiFi introduces additional latency and reliability variables.
Monitor jitter, latency, and packet loss continuously using network monitoring tools. Jitter should stay below 30 milliseconds, latency under 150 milliseconds, and packet loss below 1% for acceptable call quality. When metrics exceed these thresholds, investigate and resolve the underlying causes.
Choose the appropriate audio codec for your needs. Codecs like G.711 provide excellent voice quality but require more bandwidth, while G.729 compresses audio to use less bandwidth at the cost of slight quality reduction. Test different codecs to find the best balance for your network capabilities.
Implement redundancy and failover mechanisms to maintain service during outages. Configure automatic failover to backup internet connections if your primary service fails. Cloud-based VoIP systems often include built-in redundancy across multiple data centers for enhanced reliability.
Deploy Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) units for your network equipment and VoIP phones. These battery backup systems keep critical infrastructure running during power outages long enough to maintain communications or conduct orderly shutdowns.
Consider hybrid solutions that combine VoIP with traditional phone lines for critical functions like emergency services, alarm systems, or key customer service lines. This redundancy ensures you maintain some communication capability even if your internet fails completely.
Work closely with your Internet Service Provider (ISP) to establish Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that guarantee uptime percentages and response times for outages. Choose business-grade internet services rather than residential plans for better reliability and support.
Conclusion: Overcoming VoIP Integration Challenges Successfully
Integrating VoIP into your business infrastructure presents genuine challenges, but each obstacle has practical solutions. By addressing legacy compatibility through thorough planning and the right tools, ensuring adequate network resources with QoS configuration, implementing robust security measures, investing in change management and training, and establishing reliable infrastructure with redundancy, you can successfully navigate the transition.
The key to smooth VoIP integration lies in preparation. Assess your current environment honestly, allocate sufficient resources for implementation and training, choose providers with strong support and integration capabilities, and maintain realistic timelines that allow for testing and adjustment.
When implemented thoughtfully, VoIP systems deliver substantial benefits including reduced telecommunications costs, enhanced mobility for remote workers, advanced features that boost productivity, better scalability as your business grows, and unified communications that integrate voice, video, and messaging.
Don’t let integration challenges deter you from modernizing your business communications. With the strategies outlined in this guide, you can overcome common obstacles and position your organization to leverage the full potential of VoIP technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How much bandwidth do I need for VoIP in my business?
Plan for approximately 100 kbps per concurrent call, though this varies based on the codec used. For a business with 20 employees where 10 might be on calls simultaneously, you’d need at least 1 Mbps dedicated to VoIP. However, it’s wise to have substantially more total bandwidth to account for other internet activities and provide a quality buffer. Most businesses find that 25-50 Mbps or higher works well for mixed usage including VoIP.
Can I keep my existing phone numbers when switching to VoIP?
Yes, you can keep your existing phone numbers through a process called number porting. Most VoIP providers handle this transfer, which typically takes 2-4 weeks to complete. You’ll need to provide authorization and account information from your current carrier. The process is regulated to protect your right to keep your numbers, so providers must facilitate legitimate porting requests.
What happens to my VoIP phones during a power outage?
VoIP phones require electricity to function, so they’ll stop working during power outages unless you have backup power. Install Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) units for your network equipment, routers, and phones to maintain service during brief outages. For extended outages, consider hybrid solutions that include traditional phone lines for critical functions, or use softphone applications on mobile devices that can route calls over cellular data networks.
Is VoIP secure enough for confidential business conversations?
Yes, when properly implemented, VoIP can be very secure. Look for providers offering end-to-end encryption using protocols like TLS and SRTP. Implement strong authentication, regular security updates, and Session Border Controllers for additional protection. For highly sensitive industries like healthcare or finance, choose providers with relevant compliance certifications and features like encrypted call recording and secure storage.
How long does it take to fully integrate VoIP into a business?
Integration timelines vary based on company size and complexity. Small businesses with simple needs might complete integration in 2-4 weeks. Mid-sized companies typically need 1-3 months for planning, implementation, and training. Large enterprises with complex legacy systems may require 3-6 months or longer. Phased rollouts generally work better than attempting to switch everything simultaneously.
Will VoIP work with my existing CRM and business software?
Most modern VoIP solutions offer integrations with popular business platforms like Salesforce, HubSpot, Microsoft Teams, Zendesk, and others. Check with your VoIP provider about specific integrations before committing. Many providers offer APIs that allow custom integrations with proprietary software. If you use specialized or legacy software, discuss integration requirements with the provider during the evaluation phase.
What’s the difference between on-premises and cloud-based VoIP?
On-premises VoIP requires you to purchase and maintain physical equipment (servers, PBX hardware) at your location, giving you complete control but requiring IT expertise and upfront capital investment. Cloud-based VoIP (hosted VoIP) is managed by the provider in their data centers, offering lower upfront costs, easier scalability, automatic updates, and reduced maintenance burden. Most small to medium businesses find cloud-based solutions more cost-effective and manageable.
Can remote employees use the business VoIP system?
Absolutely. VoIP excels at supporting remote work. Employees can use softphone applications on their computers or mobile devices, or physical IP phones at home offices that connect through the internet. Remote workers get the same features as in-office staff including extension dialing, call transfers, and access to business numbers. This flexibility is one of VoIP’s biggest advantages over traditional phone systems.
What quality issues might I experience with VoIP and how can I prevent them?
Common quality issues include choppy audio, delays, echo, and dropped calls. These usually stem from insufficient bandwidth, network congestion, or poor QoS configuration. Prevent problems by ensuring adequate bandwidth, implementing QoS to prioritize voice traffic, using wired connections instead of WiFi for desk phones, monitoring network performance regularly, and choosing quality equipment designed for VoIP. Most quality issues are preventable with proper network configuration.
How much can my business save by switching to VoIP?
Savings vary widely but most businesses reduce telecommunications costs by 30-50% after switching to VoIP. You’ll save on long-distance and international calling fees, reduce hardware maintenance costs, eliminate separate systems for voice and data, and benefit from easier scalability that prevents overprovisioning. Cloud-based VoIP eliminates expensive PBX equipment purchases and ongoing maintenance contracts. Factor in improved productivity from advanced features when calculating total value.







No comment